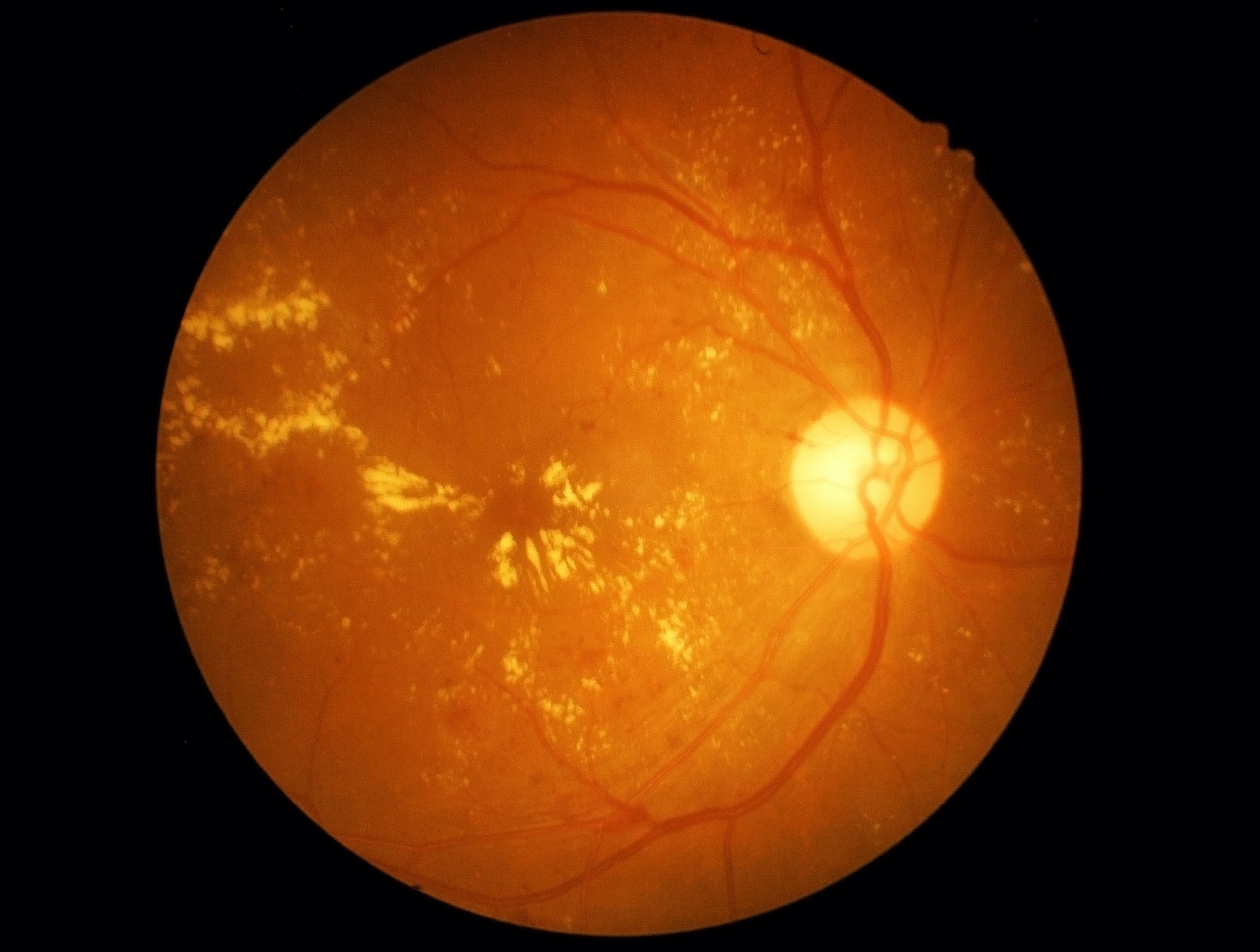
Diabetic Retinopathy is characterized as damage to the blood vessels in the back of your eye. If you have diabetes, you are at risk for developing diabetic retinopathy and, if left untreated, it may lead to vision loss or blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is currently the leading cause of vision loss in the United States.
When you first develop diabetic retinopathy, you may not notice symptoms. As the disease progresses it can cause vision loss. The most common symptoms of diabetic retinopathy include:
A consequence of elevated blood sugar over a prolonged period of time weakens the walls of the blood vessels that provide nourishment to the retina. When the retina wall becomes weak it causes the vessels to leak fluid and blood, which in turn cause swelling in the surrounding tissue. As the disease progresses and more blood vessels are damaged, your body attempts to restore healthy blood flow by building new vessels. Unfortunately, this only exacerbates the problem as they are abnormally fragile. The new and fragile blood vessels easily bleed.
If the newly formed blood vessels associated to retinopathy bleed into the clear, gel-like vitreous fluid fill the center of your eye, a hemorrhage can occur. You may notice dark spots in your vision. A severe bleed into the vitreous may cause a vitreous hemorrhage. A hemorrhage related to retinopathy can cause temporary vision loss and may take several weeks to months to resolve.
If indicated by our specialists, it may be recommended that you undergo an in-office treatment which may include:
Sources: American Academy of Ophthalmology and Krames